Google Page Speed – What may be the easiest way to boost your pagespeed insights ’s conversion rate has nothing to do with improving your headline or changing the color of your CTA button. Instead, it’s about delivering a faster user experience.
Research from Google has uncovered a connection between conversion rate and load time. It also reveals you may be losing half your prospects to a lagging post-click landing page. Luckily, there’s a tool you can use to determine what’s slowing it down.
After clicking through 900,000 ads, researchers from Google discovered that the average mobile post-click landing page loads in an embarrassing 22 seconds. That’s over 7 times longer than most impatient internet users will wait before they abandon a page — 53% to be exact.
If your page takes more than 3 seconds to load, more than half your prospects are leaving before they even see it. As if that weren’t bad enough, the study found that with each passing second a page doesn’t load, even more visitors will bounce:
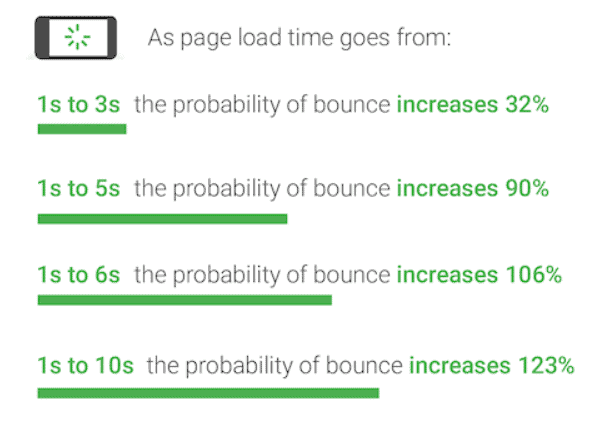
With the help of machine-learning technology from SOASTA, researchers found a correlation between load time, page weight (size in data), and conversion rate. Basically, “heavier” means slower. Specifically, when the number of elements (text, images, etc.) on a page increases from 400 to 6,000, your chances of converting a visitor drop by 95%.
How can you improve your Google page speed?
1. Avoid post-click landing page redirects
If your page hasn’t been designed responsively, the result could be a number of redirects to pages optimized for different devices. Some common redirect patterns, according to Google:
- example.com uses responsive web design, no redirects are needed – fast and optimal!
- anotherexample.com → m.anotherexample.com/home – multi-roundtrip penalty for mobile users.
- otherexample.com → www.otherexample.com → m.example.com – very slow mobile experience.
Each time a user has to be redirected, page rendering comes to a halt — which adds precious seconds to your page’s load time. Avoid redirects altogether by building your pages with responsive design — a method that ensures quality user experience no matter the device your prospect is on.
2. Enable compression
Today’s browsers are capable to serve a smaller alternative version of a page to internet users. With the compressor gzip enabled, those pages can shrink in size by 90%.
When compression is enabled, though, the process looks more like this:
Instead of serving the user the full page, the browser can fetch an exponentially smaller compressed version that loads in a fraction of the time. Learn more about optimizing with gzip here.
3. Minify CSS, HTML, JavaScript
“Minifying” refers to removing unnecessary or redundant data without affecting how the page is processed by the browser. Poor coding can be the cause of this problem, and it can be fixed a few different ways.
Outside of surveying your page’s source code manually,you may try Fast Velocity Minify for your WordPress Sites.
4. Prioritize above-the-fold content
As strange as this may seem, page load time isn’t solely about how quickly your page loads. It’s also about “perceived performance.”
To boost perceived performance, it’s crucial to prioritize the loading of content important to the user. For example, a page’s text above the fold should load before third-party widgets.
When the code is structured incorrectly, though, the result can be decreased perceived performance in the mind of the user. If the last elements on your page to load are the ones the user clicked through to see, the page will feel like it loads longer.
5. Speed up server response time
Server response time — the time it takes for your server to begin loading a page’s content for a user — it can slow down by a number of factors according to Google:
- Database queries
- Slow routing
- Frameworks
- Libraries
- Resource CPU starvation
- Memory starvation
Try for the sub-200ms server response time that Google recommends. Consider doing the same, or upgrading your current web hosting package to a more capable plan.
6. Eliminate render-blocking JavaScript
Among other things, JavaScript enables some powerful third-party tools and interactive page elements. The trouble with it is, it also halts the parsing of HTML code.
When you see an error message that reads “eliminate render-blocking JavaScript,” it means there’s a piece of JavaScript code that’s pausing the loading process for the above-fold portion of your page. Third-party scripts in particular are likely to blame for this problem. Tackle it three ways:
Scripts that aren’t crucial to the loading process should be purposely delayed — fetched and executed after the page is fully rendered.
Scripts that load asynchronously should be used over ones that load synchronously. Synchronous scripts pause the page-rendering process, while asynchronous ones allow a browser to load other elements at the same time
Consider inlining the script — inserting small external JavaScript resources directly into your HTML document — to reduce the number of requests your browser has to make.
7. Leverage browser caching
It can take multiple requests between a server and browser before a page fully loads for a user. As far as time is concerned, each one adds up.
When you cache it allows your browser to, in a way, “remember” certain elements that have been recently loaded — header, navigation, logo, etc. The more elements the browser can cache, the fewer elements it has to load the moment the user makes a request, and ultimately, the faster a page will load.
Google recommends a minimum caching policy of one week, and for elements that go largely unchanged, one year is preferable.
8. Optimize images
In a blog post, Google testers specifically warned of the threat that images pose to page speed. “Graphic elements such as favicons, logos, and product images can easily comprise up to two-thirds of a page’s total weight,” they said.
When that happens, the effect on page load time, and specifically conversion rate, is huge. According to the study, pages that converted visitors contained 38% fewer images than the ones that didn’t:
Fortunately, optimizing images is easy. The replacement of a PNG with a JPEG image file can easily save your page size and load time. So can image compressors like Google’s Guetzli and Zopfli.
But before you use those, ask yourself if you really need all the images you’ve included on your page. Are they really adding value, or could you do without them? If the answer is the latter, scrap them altogether to save data and time.
That was all for today in the article easy guide to improve your Google Page Speed.







Thanks for the nice tutorial. I have implemented it and seems to be working fine as far as my website is considered.
Good to hear that.
Thanks a lot… It was really helpful for my website.
Pleasure is all ours… Good to know that it was helpful